
China, Russia and the bomb

Alliance ruffled by dispute over nuclear weapons
By Lawrence S. Wittner
Even international alliances can unravel when nations confront the insanity of a nuclear holocaust.
An illustration of this point occurred last September when Vladimir Putin once again threatened Ukraine and other nations with nuclear war.
“To defend Russia and our people, we doubtlessly will use all weapons resources at our disposal,” the Russian president said. “This is not a bluff.”
In response to this statement and to sharp UN condemnation of Russian nuclear threats, Chinese president Xi Jinping issued a public statement in November, assailing “the use of, or threats to use nuclear weapons.” To “prevent a nuclear crisis” in Europe or Asia, he insisted, the world should “advocate that nuclear weapons cannot be used” and “a nuclear war cannot be waged.”
Aren’t these two nuclear-armed nations currently aligned in their resistance to U.S. foreign policy? Yes, they are, and when it came to Putin’s war upon Ukraine, Xi refrained from suggesting a Russian withdrawal. But nuclear war, as the Chinese leader made clear, was simply not acceptable.
This was not the first time a Russian-Chinese alliance was ruffled by a dispute over the use of nuclear weapons. An even deeper conflict occurred during the late 1950s and early 1960s when, ironically, the roles of the two nations were exactly the reverse.
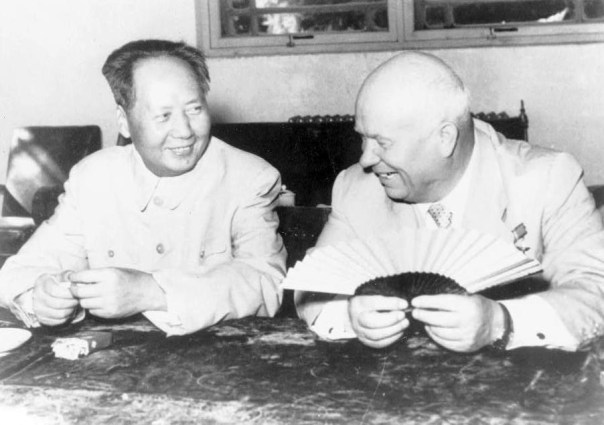

At that time, the Chinese government, led by Mao Zedong, was embarked on a crash program to develop nuclear weapons. In October 1957, China’s weapons program secured a major gain when the Russian and Chinese governments signed the New Defense Technical Accord, in which the Russians agreed to supplementing the nuclear assistance they had already provided to the Chinese by supplying them with a prototype atomic bomb, missiles, and useful technical data.
Read MoreClean energy or weapons?

What the ‘breakthrough’ in nuclear fusion really means
By M.V. Ramana
On December 13, the US Department of Energy (DOE) announced that the National Ignition Facility (NIF) at the Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory had reached a “milestone”: the achievement of “ignition” in nuclear fusion earlier in the month. That announcement was hailed by many as a step into a fossil fuel-free energy future. US Senate majority leader Charles Schumer, for example, claimed that we were “on the precipice of a future no longer reliant on fossil fuels but instead powered by new clean fusion energy”.
But in truth, generating electrical power from fusion commercially or at an industrial scale is likely unattainable in any realistic sense, at least within the lifetimes of most readers of this article. At the same time, this experiment will contribute far more to US efforts to further develop its terrifyingly destructive nuclear weapons arsenal.
Over the last decade or so, there have been many similar announcements featuring breathless language about breakthroughs, milestones, and advances. These statements have come with unfailing regularity from NIF (for example, in 2013) and the larger set of laboratories and commercial firms pursuing the idea of nuclear fusion. Apart from the United States, similar announcements have come from Germany, China and the United Kingdom. France is expected to take its turn once the International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor (ITER) starts operating. The reactor is currently being built in Cadarache, France, at an estimated cost of somewhere between $25 billion to as high as $65 billion, much higher than the original estimate of $5.6 billion.
These incredibly high costs also explain why such announcements are made in the first place: without the excitement created by these hyped-up statements, it would be impossible to get funded for the decades it takes to plan and build these facilities. Conceptual design work on ITER began in 1988.
Of course, that timescale pales in comparison to the time period of the first major announcement about fusion-generated electricity. That took place in 1955 when Homi Bhabha, the architect of India’s nuclear programme, told the first International Conference on Peaceful Uses of Atomic Energy in Geneva:
“I venture to predict that a method will be found for liberating fusion energy in a controlled manner within the next two decades. When that happens the energy problems of the world will have been solved for ever.”
That would not be the last prediction about the imminence of fusion power that would be wrong.
Read MoreWhat’s all the fuss about fusion?

Was there really just a breakthrough, and if so, for whom?
By Linda Pentz Gunter
It was heralded as a major breakthrough. The tantalizing challenge of fusion had been cracked! Yes, the elusive moment when the fusing of atoms would release more energy than had been put in, had finally happened. The National Ignition Facility at Lawrence Livermore Laboratory in California had won the fusion race against hot competition both in the US and overseas.
This “landmark achievement,” as U.S. energy secretary, Jennifer Granholm, described it, now means that what had been forever decades away — the delivery of electricity powered by fusion — was now……still decades away.
The Washington Post aptly summed up all the hype in a single sentence: “This was a science experiment more than a demonstration of a practical technology.” The New Statesman echoed the hype angle.

And how big a breakthrough really was it? While the experiment delivered 3.15 megajoules of energy output to the 2.05 megajoules it put in, the 192 lasers that produced it required 300 megajoules of energy.
We have been here before, as described in Stephane Lhomme’s accompanying article (in English and French.) For example, back in 1991, the collaborative Joint European Torus (JET) project in the UK achieved a temperature of about 200 million degrees Celsius (about 10 times the temperature in the centre of the sun) for a period of two seconds. Thermonuclear energy from a deuterium-tritium plasma (86% deuterium and 14% tritium) was released during this time at the rate of 2 million watts.
This, too, was heralded as “a significant milestone”, by JET’s director at the time, Dr Paul-Henri Rebut. Since then, there have been a series of other so-called breakthroughs, none of which have brought us any closer to the practical application of fusion as a provider of commercial electricity.
Read MoreThe grand illusion

Money talks and the gullible have bought the bluster about fusion
By Stéphane Lhomme
Competition is raging between the teams working in various countries on nuclear fusion. However, this rivalry does not play out on the scientific fields that now lie fallow, but merely at the public relations the level. It is all about announcing a “decisive advance” at the best moment to obtain large budgets and to be able to continue research that is certainly exciting for physicists, but completely useless as a practical reality.
Back on November 12, 1991, the daily Le Monde ran the headline “The Europeans take a decisive step in thermonuclear fusion”, before reporting on December 12, 1993 on the “counter-attack” by the USA (still just a war of words): “The Americans make a breakthrough in thermonuclear fusion”.
Thirty years later, the same publicity stunt was published in the same newspaper, which announced on December 13, 2022 “Nuclear fusion: a ‘major scientific breakthrough’ announced by an American laboratory”.
La grande illusion

Fusion nucléaire : une énième “avancée décisive” pour abuser les gogos… et décrocher de nouveaux budgets
De Stéphane Lhomme
La concurrence fait rage entre les équipes qui travaillent dans divers pays sur la question de la fusion nucléaire. Cependant, cette rivalité n’a pas lieu sur le terrain scientifique, en jachère, mais sur le seul plan de la communication. Il s’agit en effet d’annoncer une “avancée décisive” au meilleur moment permettant de se faire attribuer d’importants budgets et pouvoir continuer des recherches qui sont assurément passionnantes pour les physiciens, mais en réalité parfaitement vaines.
Le 12 novembre 1991, le quotidien Le Monde titrait “Les Européens franchissent un pas décisif dans la fusion thermonucléaire” avant de rendre compte le 12 décembre 1993 de la “contre-attaque” des USA (toujours sur le terrain de la communication) : “Les Américains effectuent une percée dans la fusion thermonucléaire”.
Trente ans plus tard, les mêmes effets d’annonce sont de mise et le même journal annonce le 13 décembre 2022 “Fusion nucléaire : une « percée scientifique majeure » annoncée par un laboratoire américain”.

Are the bombs are back in town?

Is the US about to station nuclear weapons in Britain again or are they already here?
From Campaign for Nuclear Disarmament (CND UK)
Editor’s Note: A mass demonstration organized by CND was held at Lakenheath, Suffolk, United Kingdom on November 19. “It’s extraordinary that a foreign power can place weapons of mass destruction on our soil with no oversight from our elected representatives,” said Sue Wright from Norwich CND (Norwich is 40 miles from the base). For more background, see our May 15, 2022 article by CND General Secretary, Kate Hudson, CND’s special page on the Lakenheath campaign, and this article by Hans Kristensen for Federation of American Scientists.
Beyond Nuclear, International Physicians for the Prevention of Nuclear War, Peace Action and Nuclear Resister, sent a joint statement of solidarity that was read out at the November 19 protest.
CND condemns any return of United States nuclear weapons to RAF Lakenheath in Suffolk. 110 nuclear bombs were stored at the airbase until they were removed in 2008 following persistent popular protest, and they must not be allowed back.
Response to war
Tensions are rising across Europe amidst the ongoing war in Ukraine. In response to the Russian invasion, reports are circulating that the US is preparing to store some of its nuclear weapons in the UK. This originated with the fact that the US Department of Defense has added the UK to a list of NATO nuclear weapons storage locations in Europe being upgraded under a multimillion-dollar infrastructure programme. The UK was not on the comparable list for the previous year, so this looks like a very recent decision.
Experts now believe the base in question is RAF Lakenheath, located just 100 km from London.

History repeats itself
While it is not yet known if nuclear weapons have already been returned to the base, or if NATO is in the process of preparing the base to be ready to receive them, this development marks a change in the nuclear status of RAF Lakenheath.
RAF Lakenheath hosted US nuclear weapons for more than five decades, first arriving in September 1954. CND arranged protests at the base alongside the Lakenheath Action Group, including days of action where hundreds of people descended on the base. Direct action activists broke into the base and locked on to the gates of the ammunition depot, preventing access for hours.
Messages of support were shared between campaigners at other US bases in Europe, and from Faslane, where Britain’s nuclear weapons are stationed. Plays were presented outside the base, and letters handed in to the Commander.
Following years of protesting, the nuclear weapons were eventually removed in 2008, but not before nuclear accidents endangered the safety of the local community.
Read More Beyond Nuclear International
Beyond Nuclear International