
Does Britain really need nuclear power?

It doesn’t, but the link to nuclear weapons is the key driver, writes Ian Fairlie
In recent months, the government has continued to promote nuclear reactors. For example, the Energy Secretary is now asking GB Energy to assess sites to be used to host new nuclear reactors. And the Prime Minister continues to push for so-called Small Modular Reactors and has backed the US President’s wishful thinking of ‘a golden age of nuclear’.
But these announcements and proposals are mostly pie-in-the-sky statements and should be treated with a pinch (or more) of salt, as the reality is otherwise.
Let’s look at what is happening in the rest of the world. Last year, a record 582 GW of renewable energy generation capacity was added to the world’s supplies: almost no new nuclear was added.
Indeed, each year, new renewables add about 200 times more global electricity than new nuclear does.
Of course, there are powerful economic arguments for this. The main one is that the marginal (i.e. fuel) costs of renewable energy are close to zero, whereas nuclear fuel is extremely expensive. Nuclear costs – for both construction and generation – are very high and rising, and long delays are the norm. For example, the proposed Sizewell C nuclear station is now predicted to cost £47 billion, with the government and independent experts acknowledging even this estimate may rise significantly. The upshot is that new nuclear power means massive costs, a poisoned legacy to future generations, and whopping radioactive pollution.

Ministry of Housing, Communities and Local Government/Wikimedia Commons)
Given these manifest disadvantages, independent commentators have questioned the government’s seeming obsession with nuclear power. It is not that nuclear provides a good solution to global warming: it doesn’t. The United Nations’ Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) reports that renewables are now 10 times more efficient than new nuclear at CO2 mitigation.
Read MoreNuclear power will never be “beneficial”

Abandoning radiation protection will further endanger vulnerable populations, writes Cindy Folkers
As its name suggests, the Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) was created to regulate the nuclear power industry in order to protect people and the environment from the inherent dangers of that technology. As much as the NRC is currently failing to fully meet this mission, recent political maneuvers to curtail its influence threaten public health and safety even further.
A May 23 executive order from President Trump will now transform the stated mission of NRC from safety regulator to industry enabler, and in fact, NRC mission wording has been changed to say that nuclear power “benefits” society, despite the evidence to the contrary given the often serious health impacts of all nuclear power-related operations. This mission shift has sparked alarm among experts and safety advocates who argue that abandoning core principles of radiation protection will further endanger communities, sacrifice vulnerable populations, and increase the nuclear industry’s grip on energy policy.
The slate of executive orders issued by President Trump on May 23 are designed to “fast-track everything nuclear.” Beyond Nuclear has already highlighted the many concerns posed by these orders. For example, EO 14300 – titled Ordering the Reform of the Nuclear Regulatory Commission – will weaken radiation exposure standards, posing grave risks to public health from nuclear technology.
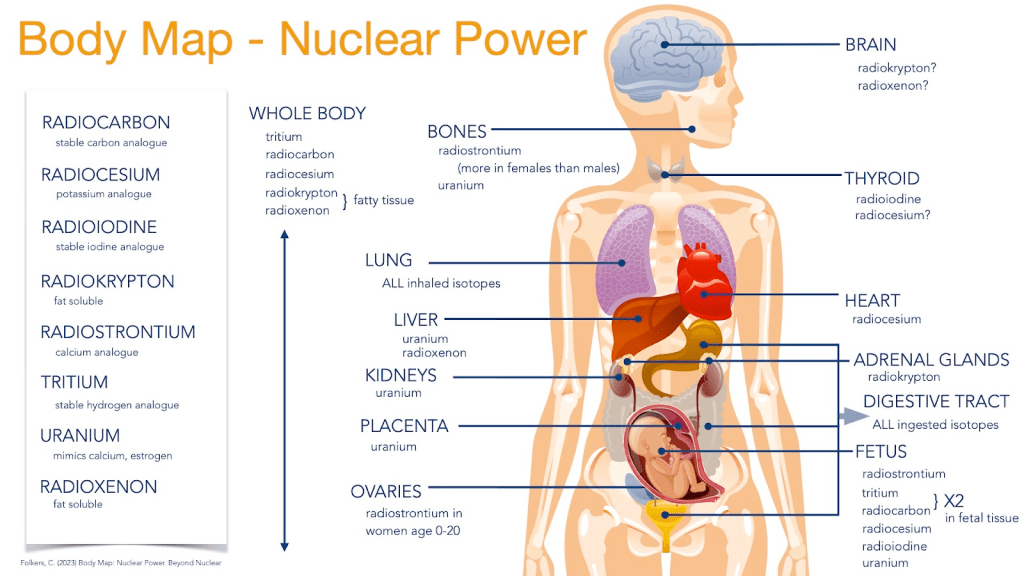
Among the decades of hard-won protections this executive order undermines is the scientifically supported foundation that there is no safe level of radiation exposure. The changes threaten not just U.S. regulatory integrity but global public health and environmental safety.
Section 5(b) of EO 14300 is particularly alarming. It calls on the NRC to adopt “science-based radiation limits” and demands the NRC reconsider its longstanding reliance on the Linear No Threshold (LNT) model. But in effect, this request contradicts itself.
Read MoreBritain’s “borrowed bombs”

New reports shows UK purchase of US nuclear-capable aircraft is political grandstanding with little practical application, writes Linda Pentz Gunter
When the UK government announced its intention last June to purchase 12 F-35A nuclear capable Lightning II Joint Strike Fighter aircraft from the US by 2033 and join NATO’s ‘dual capable aircraft nuclear mission’, it described the decision as the “biggest strengthening of the UK’s nuclear posture in a generation”.
But a new study released on November 11 by two British watchdog groups, Nukewatch UK and Nuclear Information Service, argues that the purchase of the planes will incur massive costs to the British taxpayer while not actually being militarily necessary or advantageous.
The report, “Smoke andMirrors”, concludes that “the government’s decision is based principally on providing political ‘smoke and mirrors’ to distract attention from questions relating to the US-Europe relationship within NATO rather than developing a must-have military capability.”

The purchase of the F35As “serves more as a diplomatic gesture than a military imperative,” the study said, designed to placate US president Donald Trump’s gripes about a perceived lack of financial commitment from NATO partners.
The UK decision to participate in the NATO nuclear sharing mission “is being driven forward by the nuclear lobby within government itself, and raises questions about whether the decision was driven by strategic necessity or political expediency,” the study authors wrote.
Read MoreThe Big-Tech Warmongers’ American Dream

What they envisage would be a nightmare for the rest of us, writes William Hartung
Editor’s note: Since this article was first published on Common Dreams, Elon Musk is no longer wielding the metaphorical axe at DOGE, and DOGE has reportedly been disbanded, but the policies of cuts and purges continues.
Alex Karp, the CEO of the controversial military tech firm Palantir, is the coauthor of a new book, The Technological Republic: Hard Power, Soft Belief, and the Future of the West. In it, he calls for a renewed sense of national purpose and even greater cooperation between government and the tech sector. His book is, in fact, not just an account of how to spur technological innovation, but a distinctly ideological tract.
As a start, Karp roundly criticizes Silicon Valley’s focus on consumer-oriented products and events like video-sharing apps, online shopping, and social media platforms, which he dismisses as “the narrow and the trivial.” His focus instead is on what he likes to think of as innovative big-tech projects of greater social and political consequence. He argues, in fact, that Americans face “a moment of reckoning” in which we must decide “what is this country, and for what do we stand?” And in the process, he makes it all too clear just where he stands—in strong support of what can only be considered a new global technological arms race, fueled by close collaboration between government and industry, and designed to preserve America’s “fragile geopolitical advantage over our adversaries.”
Karp believes that applying American technological expertise to building next-generation weapons systems is not just a but the genuine path to national salvation, and he advocates a revival of the concept of “the West” as foundational for future freedom and collective identity. As Sophie Hurwitz of Mother Jones noted recently, Karp summarized this view in a letter to Palantir shareholders in which he claimed that the rise of the West wasn’t due to “the superiority of its ideas or values or religion… but rather by its superiority in applying organized violence.”
Count on one thing: Karp’s approach, if adopted, will yield billions of taxpayer dollars for Palantir and its militarized Silicon Valley cohorts in their search for AI weaponry that they see as the modern equivalent of nuclear weapons and the key to beating China, America’s current great power rival.
Militarism as a Unifying Force
Karp may be right that this country desperately needs a new national purpose, but his proposed solution is, to put it politely, dangerously misguided.
Ominously enough, one of his primary examples of a unifying initiative worth emulating is World War II’s Manhattan Project, which produced the first atomic bombs. He sees the building of those bombs as both a supreme technological achievement and a deep source of national pride, while conveniently ignoring their world-ending potential. And he proposes embarking on a comparable effort in the realm of emerging military technologies: “The United States and its allies abroad should without delay commit to launching a new Manhattan Project in order to retain exclusive control of the most sophisticated forms of AI for the battlefield—the targeting systems and swarms of drones and robots that will become the most powerful weapons of the century.”
And here’s a question he simply skips: How exactly will the United States and its allies “retain exclusive control” of whatever sophisticated new military technologies they develop? After all, his call for an American AI buildup echoes the views expressed by opponents of the international control of nuclear technology in the wake of the devastating atomic bombings of the Japanese cities of Hiroshima and Nagasaki that ended World War II—the futile belief that the United States could maintain a permanent advantage that would cement its role as the world’s dominant military power.
Nearly 80 years later, we continue to live with an enormously costly nuclear arms race—nine countries now possess such weaponry—in which a devastating war has been avoided as much thanks to luck as design. Meanwhile, past predictions of permanent American nuclear superiority have proven to be wishful thinking. Similarly, there’s no reason to assume that predictions of permanent superiority in AI-driven weaponry will prove any more accurate or that our world will be any safer.
Technology Will Not Save Us
Karp’s views are in sync with his fellow Silicon Valley militarists, from Palantir founder Peter Thiel to Palmer Luckey of the up-and-coming military tech firm Anduril to America’s virtual co-president, SpaceX’s Elon Musk. All of them are convinced that, at some future moment, by supplanting old-school corporate weapons makers like Lockheed Martin and Northrop Grumman, they will usher in a golden age of American global primacy grounded in ever better technology. They see themselves as superior beings who can save this country and the world, if only the government—and ultimately, democracy itself—would get out of their way. Not surprisingly, their disdain for government does not extend to a refusal to accept billions and billions of dollars in federal contracts. Their anti-government ideology, of course, is part of what’s motivated Musk’s drive to try to dismantle significant parts of the federal government, allegedly in the name of “efficiency.”

An actual efficiency drive would involve a careful analysis of what works and what doesn’t, which programs are essential and which aren’t, not an across-the-board, sledgehammer approach of the kind recently used to destroy the U.S. Agency for International Development (USAID), to the detriment of millions of people around the world who depended on its programs for access to food, clean water, and healthcare, including measures to prevent the spread of HIV-AIDS. Internal agency memos released to the press earlier this month indicated that, absent USAID assistance, up to 166,000 children could die of malaria, 200,000 could be paralyzed with polio, and 1 million of them wouldn’t be treated for acute malnutrition. In addition to saving lives, USAID’s programs cast America’s image in the world in a far better light than does a narrow reliance on its sprawling military footprint and undue resort to threats of force as pillars of its foreign policy.
As a military proposition, the idea that swarms of drones and robotic systems will prove to be the new “miracle weapons,” ensuring American global dominance, contradicts a long history of such claims. From the “electronic battlefield” in Vietnam to former President Ronald Reagan’s quest for an impenetrable “Star Wars” shield against nuclear missiles to the Gulf War’s “Revolution in Military Affairs” (centered on networked warfare and supposedly precision-guided munitions), expressions of faith in advanced technology as the way to win wars and bolster American power globally have been misplaced. Either the technology didn’t work as advertised; adversaries came up with cheap, effective countermeasures; or the wars being fought were decided by factors like morale and knowledge of the local culture and terrain, not technological marvels. And count on this: AI weaponry will fare no better than those past “miracles.”
First of all, there is no guarantee that weapons based on immensely complex software won’t suffer catastrophic failure in actual war conditions, with the added risk, as military analyst Michael Klare has pointed out, of starting unnecessary conflicts or causing unintended mass slaughter.
Second, Karp’s dream of “exclusive control” of such systems by the U.S. and its allies is just that—a dream. China, for instance, has ample resources and technical talent to join an AI arms race, with uncertain results in terms of the global balance of power or the likelihood of a disastrous U.S.-China conflict.
Third, despite Pentagon pledges that there will always be a “human being in the loop” in the use of AI-driven weaponry, the drive to wipe out enemy targets as quickly as possible will create enormous pressure to let the software, not human operators, make the decisions. As Biden administration Air Force Secretary Frank Kendall put it, “If you have a human in the loop, you will lose.”
Automated weapons will pose tremendous risks of greater civilian casualties and, because such conflicts could be waged without putting large numbers of military personnel at risk, may only increase the incentive to resort to war, regardless of the consequences for civilian populations.
What Should America Stand For?
Technology is one thing. What it’s used for, and why, is another matter. And Karp’s vision of its role seems deeply immoral. The most damning real-world example of the values Karp seeks to promote can be seen in his unwavering support for Israel’s genocidal war on Gaza. Not only were Palantir’s systems used to accelerate the pace of the Israeli Defense Force’s murderous bombing campaign there, but Karp himself has been one of the most vocal supporters of the Israeli war effort. He went so far as to hold a Palantir board meeting in Israel just a few months into the Gaza war in an effort to goad other corporate leaders into publicly supporting Israel’s campaign of mass killing.
Are these really the values Americans want to embrace? And given his stance, is Karp in any position to lecture Americans on values and national priorities, much less how to defend them?
Despite the fact that his company is in the business of enabling devastating conflicts, his own twisted logic leads Karp to believe that Palantir and the military-tech sector are on the side of the angels. In May 2024, at the “AI Expo for National Competitiveness,” he said of the student-encampment movement for a cease-fire in Gaza, “The peace activists are war activists. We are the peace activists.”
Invasion of the Techno-Optimists
And, of course, Karp is anything but alone in promoting a new tech-driven arms race. Elon Musk, who has been empowered to take a sledgehammer to large parts of the U.S. government and vacuum up sensitive personal information about millions of Americans, is also a major supplier of military technology to the Pentagon. And Vice President JD Vance, Silicon Valley’s man in the White House, was employed, mentored, and financed by Palantir founder Peter Thiel before joining the Trump administration.
The grip of the military-tech sector on the Trump administration is virtually unprecedented in the annals of influence-peddling, beginning with Elon Musk’s investment of an unprecedented $277 million in support of electing Donald Trump and Republican candidates for Congress in 2024. His influence then carried over into the presidential transition period, when he was consulted about all manner of budgetary and organizational issues, while emerging tech gurus like Marc Andreessen of the venture capital firm Andreessen Horowitz became involved in interviewing candidates for sensitive positions at the Pentagon. Today, the figure who is second-in-charge at the Pentagon, Stephen Feinberg of Cerberus Capital, has a long history of investing in military firms, including the emerging tech sector.
But by far the greatest form of influence is Musk’s wielding of the essentially self-created Department of Government Efficiency (DOGE) to determine the fate of federal agencies, programs, and employees, despite the fact that he has neither been elected to any position, nor even confirmed by Congress, and that he now wields more power than all of Trump’s cabinet members combined.
As Alex Karp noted—no surprise here, of course—in a February 2025 call with Palantir investors, he’s a big fan of the DOGE, even if some people get hurt along the way: “We love disruption, and whatever’s good for America will be good for Americans and very good for Palantir. Disruption, at the end of the day, exposes things that aren’t working. There will be ups and downs. There’s a revolution. Some people are going to get their heads cut off. We’re expecting to see really unexpected things and to win.”
Even as Musk disrupts and destroys civilian government agencies, some critics of Pentagon overspending hold out hope that at least he will put his budget-cutting skills to work on that bloated agency. But so far the plan there is simply to shift money within the department, not reduce its near-trillion-dollar top line. And if anything is trimmed, it’s likely to involve reductions in civilian personnel, not lower spending on developing and building weaponry, which is where firms like Palantir make their money. Musk’s harsh critique of existing systems like Lockheed’s F-35 jet fighter—which he described as “the worst military value for money in history”—is counterbalanced by his desire to get the Pentagon to spend far more on drones and other systems based on emerging (particularly AI) technologies.
Of course, any ideas about ditching older weapons systems will run up against fierce resistance in Congress, where jobs, revenues, campaign contributions, and armies of well-connected lobbyists create a firewall against reducing spending on existing programs, whether they have a useful role to play or not. And whatever DOGE suggests, Congress will have the last word. Key players like Sen. Roger Wicker (R-Miss.) have already revived the Reaganite slogan of “peace through strength” to push for an increase of—no, this is not a misprint!—$150 billion in the Pentagon’s already staggering budget over the next four years.
What Should Our National Purpose Be?
Karp and his Silicon Valley colleagues are proposing a world in which government-subsidized military technology restores American global dominance and gives us a sense of renewed national purpose. It is, in fact, a remarkably impoverished vision of what the United States should stand for at this moment in history when non-military challenges like disease, climate change, racial and economic injustice, resurgent authoritarianism, and growing neofascist movements pose greater dangers than traditional military threats.

Technology has its place, but why not put our best technical minds to work creating affordable alternatives to fossil fuels, a public health system focused on the prevention of pandemics and other major outbreaks of disease, and an educational system that prepares students to be engaged citizens, not just cogs in an economic machine?
Reaching such goals would require reforming or even transforming our democracy—or what’s left of it—so that the input of the public actually made far more of a difference, and leadership served the public interest, not its own economic interests. In addition, government policy would no longer be distorted to meet the emotional needs of narcissistic demagogues, or to satisfy the desires of delusional tech moguls.
By all means, let’s unite around a common purpose. But that purpose shouldn’t be a supposedly more efficient way to build killing machines in the service of an outmoded quest for global dominance. Karp’s dream of a “technological republic” armed with his AI weaponry would be one long nightmare for the rest of us.
William D. Hartung is a Senior Research Fellow at the Quincy Institute for Responsible Statecraft, and the author most recently of “Pathways to Pentagon Spending Reductions: Removing the Obstacles.” This article was first published on Common Dreams whose content is available in the Creative Commons.
Headline photo: Elon Musk and President of Argentina Javier Milei speaking at the 2025 Conservative Political Action Conference (CPAC) at the Gaylord National Resort & Convention Center in National Harbor, Maryland. (Photo: Gage Skidmore/Wikimedia Commons.)
The opinions expressed in articles by outside contributors and published on the Beyond Nuclear International website, are their own, and do not necessarily reflect the views or positions of Beyond Nuclear. However, we try to offer a broad variety of viewpoints and perspectives as part of our mission “to educate and activate the public about the connections between nuclear power and nuclear weapons and the need to abandon both to safeguard our future.”
Competition, Conflagration, or Coexistence?

The US-China relationship doesn’t have to be MAD, writes Joseph Gerson
Just over 60 years ago, in structuring the analytical abilities of freshmen who aspired to become US diplomats, including future President Bill Clinton, professor Carroll Quigley, who taught Evolution of Civilizations, insisted that his students accept that civilizations are based on six interrelated dynamics: political, economic, military, intellectual, social, and spiritual dimensions. He also taught that in different periods of history one or more of these dimensions are most important to defend and to the exercising of power beyond the society’s borders.
That analysis applies today when the struggle for great power hegemony is rooted in economic and intellectual competition as much as in traditional, but increasingly complicated, arms races. Twenty-first century economies and militaries cannot function without rare-earth metals and magnets. The list of civil and military products that cannot be manufactured without them begins with cell phones and LED screens to F-35 fighter jets, Virginia– and Columbia-class submarines, Tomahawk missiles, radar systems, and Predator drones. China has a near monopoly over both the minerals and magnets production although Greenland—an object of US President Donald Trump’s desire—can be a future source of those minerals.
Beijing’s export controls announced in October are the economic equivalent of a 1950s nuclear weapon test, demonstrating both its possession and willingness to use this ultimate economic weapon to impose global economic domination. This was not the first time that Beijing flaunted its economic superweapon. Hardly recognized by anyone in the United States, the ban came in reaction to US Commerce Department China hawks’ announcement of new technology export bans targeted primarily against China.

Power and security have always rested on economic foundations. Slavery and the industrial revolution made the European colonial era possible. Japan’s defeat in its Pacific War was dictated by the reality that it’s GDP was one-tenth that of the United States. And, as the country lacked a modern economy, the Russian revolution was won on the slogan of “Bread and Peace.”
This century’s economic and technological developments have been no exception. China now holds the US Seventh Fleet, which has guaranteed US dominance of the Pacific Ocean—“the American Lake”—at risk from its aerial denial missiles and massive naval fleet. Russian-Ukraine drone warfare, now augmented by AI coordinated drone swarms, and by the integration of AI and cyber warfare, now place conventional military and nuclear forces at risk. So too, essential civilian infrastructures, which place water and electrical supplies at risk.
Read MoreMinnesota’s aging nukes pose national threat

More than electricity, the reactors supply a steady dose of radioactive tritium in drinking water, writes Susu Jeffrey
“Sometimes before I give a speech, I ask the audience to stand up if they or someone in their family has had cancer,” says John LaForge of Nukewatch. “Eighty percent of the audience gets up.”
The Monticello nuclear power reactor is on the Mississippi River about 35-miles northwest of Minneapolis. Xcel’s twin Prairie Island reactors, plus about 50 giant dry casks storing waste reactor fuel, are all in the floodplain of the Mississippi. This waste is sited 44 to 51 miles southeast of Minneapolis and St. Paul.
There are no plans to move the waste off-island because there is no alternative destination. In fact, 34 more concrete encased steel casks are planned. There is no national hot radioactive waste repository. Think of these waste container sites as permanent radioactive waste dumps.
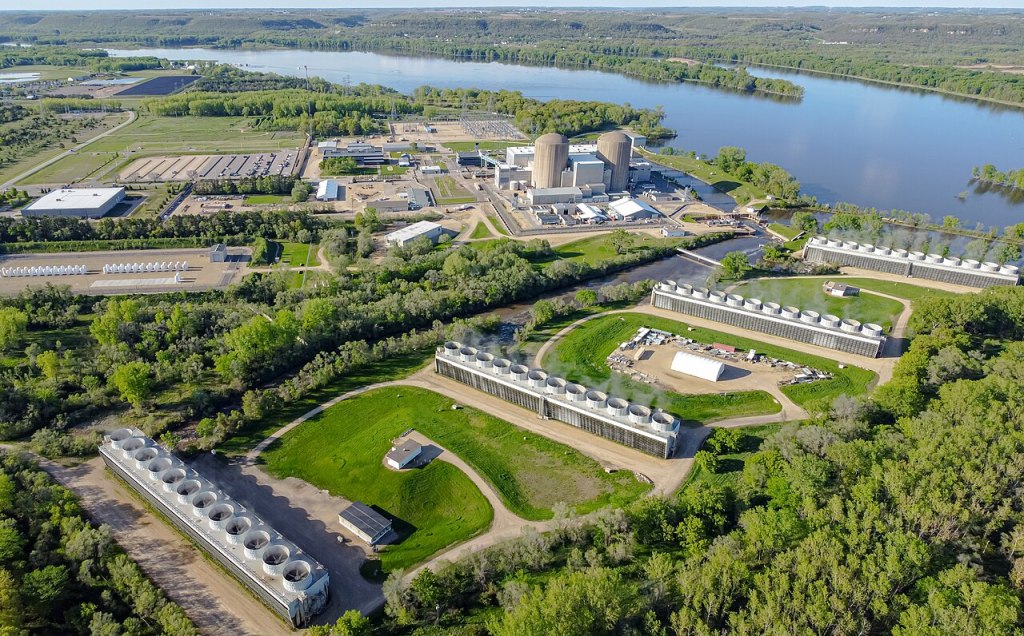

The greater Twin Cities’ 3.7 million people are in the nuclear “shadow” (within 50 miles) of all three nukes. The Mississippi River serves 20 million people with drinking water, way beyond the Minnesota state population of 5.7 million. Minnesota’s aging nukes are a national threat. For approximately the next six generations, radioactive tritium will be a part of the drinking water wherever those molecules wander.
The Monticello nuke was licensed in 1970 for 40 years, and went online in 1971, a year it had two radioactive cesium spills. In 2010, the license was renewed for another 20 years until 2030. Xcel Energy has even been granted an extension for another 20 years until 2050. It is a corporate financial security move not yet approved by the Minnesota Public Utilities Commission which holds the final consent. Paperwork is one thing, pipes are another.
Read More Beyond Nuclear International
Beyond Nuclear International